Symptoms of Heart Defects
The majority of congenital heart defects cause little to no symptoms. Even a doctor might not detect these defects during a physical exam. However, some heart defects can have quite serious effects on the baby’s well-being. This depends on the severity of the defect, the number of defects and the type of defect. In some cases, a congenital heart defect will only produce symptoms later in the child's life, which can be quite dangerous if overlooked and left untreated.
The most common symptoms may include:
 • Rapid breathing – associated with poor oxygenation (saturation with oxygen) of the blood. This triggers refractory rapid breathing as a form of compensation.
• Rapid breathing – associated with poor oxygenation (saturation with oxygen) of the blood. This triggers refractory rapid breathing as a form of compensation.
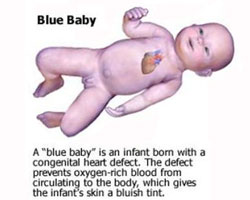
• Cyanosis – this is a very common symptom for some congenital heart defects which cause the arterial and venous blood to mix. This usually happens when there is a pathological connection between the right side of the heart and the left side heart. This symptom can be seen in patients with tetralogy of Fallot, tricuspid atresia, transposition of the great vessels, total anomalous pulmonary venous connection and persistent truncus arteriosus.
• Fatigue – fatigue may be so pronounced that the baby might not have enough strength to eat, slowing down natural weight gain and development. When the defect is less pronounced, the child may only experience this symptom later in life. This causes the child to become out of breath sooner than other children during physical activity and leads to overall weakness, under-development of muscles, and poor health.
• Syncope – is a sudden loss of consciousness. This symptom usually appears when the person performs a strenuous activity, while the heart is unable to pump enough blood to supply the brain with enough oxygen.
• Poor blood circulation – is caused by the fact that the heart is unable to pump the blood efficiently. Hypoxia (lack of oxygen) caused by poor perfusion of organs and extremities may trigger proliferation of collagen fibers. This causes a symptom known as nail clubbing – a condition during which the fingers look like drumsticks, while the nails resemble watch glass. Poor perfusion of the organs may lead to congestive hepatopathy, also known as cardiac cirrhosis.
• Heart murmurs –are characteristic heart sounds which usually occur due to leaking or narrowing valves. An abnormal passage of blood in the heart may also cause heart murmurs.
• Respiratory infections – due to poor perfusion of the lungs the bacteria are more likely to start multiplying causing various respiratory infections.
• Heart failure –many of the congenital heart defects put an additional strain on the heart which, after a time. exhausts the heart’s ability to adapt. This leads to heart failure – a condition during which the heart is unable to pump a sufficient amount of blood to meet the body’s demands. This leads to shortness of breath, fatigue during physical activity, buildup of fluid in the lungs, swelling of lower extremities and even ascites (accumulation of liquid in the abdominal cavity).
Next Chapter: Diagnosis of Congenital Heart defects









