Endocarditis
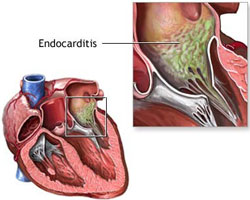
Endocarditis is an inflammation of the endocardium, the inner lining of the heart,. The structures which are involved in the inflammation process include heart valves, interventricular septum, mural endocardium and chordae tendineae. Endocarditis is characterized by vegetation, a process which involves a mass of platelets and fibrin, microcolonies of microorganisms and scarce inflammatory cells.
Endocarditis can be separated into two categories - if microorganisms are the cause of inflammation or not:
- Infective endocarditis
- Non-infective endocarditis
Non-infective Endocarditis
Non-infective endocarditis is usually caused by physical trauma. Sometimes this is clinically undetectable and it can produce emboli and impair valvular function. Physical trauma can often be caused by catheters that are passed through the right side of the heart which can cause damage to tricuspid and pulmonic valves. As a result, platelets and fibrin attach to the injury creating a lesion. Usually those lesions do not cause any valvular obstruction nor create regurgitation.
Other causes for sterile endocardial vegetations include recurrent venous thrombosis, lupus anticoagulants, stroke and spontaneous abortions.
Sterile vegetations themselves do not cause the patient to have any symptoms; however, when thrombi formed within the heart break loose, they can cause an embolization of an organ (e.g. brain, spleen, kidneys, etc.).
Treatment for non-infective endocarditis is through the use of anticoagulants including heparin or warfarin.
Infective Endocarditis
Infective endocarditis is an infection of the endocardium, which may involve one or several heart valves, mural endocardium, and eventually lead to septal defect. Infective endocarditis leads to valvular insufficiency which causes intractable (non-reversible) congestive heart failure and myocardial abscesses (a collection of neutrophils within the heart’s tissues). Infective endocarditis is fatal if left untreated.
Contents:
Causes of Endocarditis
Symptoms of Endocarditis
Diagnosis of Endocarditis
Treatment of Endocarditis
Endocarditis: Complications and Prognosis









